Organizations have different needs regarding salary components and statutory benefits. To make the most out of the session for all our attendees, we have split the entire session into two halves. The first half will cover the fundamentals of salary and statutory components in theory. The second half will take real-life examples of three different salary structures of employees belonging to various organizational hierarchy levels and show you how to configure them. By the end of the session, we hope to leave you with enough knowledge to comfortably work on Zoho payroll, creating compensation structures regardless of your organization’s policies.
Every salary structure is usually split off salary components and statutory benefits. First, let’s learn the basics of salary components. They are classified into three categories, earnings, deductions, and reimbursements.
Earnings are further classified as fixed and variable pay. All the elements come under the fixed pay, while the one-time payments, like, the annual bonus, come under the variable pay.
Deductions can be classified into two types pre-tax and post-tax. The difference between the two deductions is the tax-saving benefit for the employee. Whenever you make a pre-tax deduction, your employees won’t have to pay income tax for it. One good example of a pre-tax deduction is the group medi-claim, the insurance premium. When you make a post-tax deduction, the employees are liable to pay income tax on asset damage deduction is an example of a post-tax deduction.
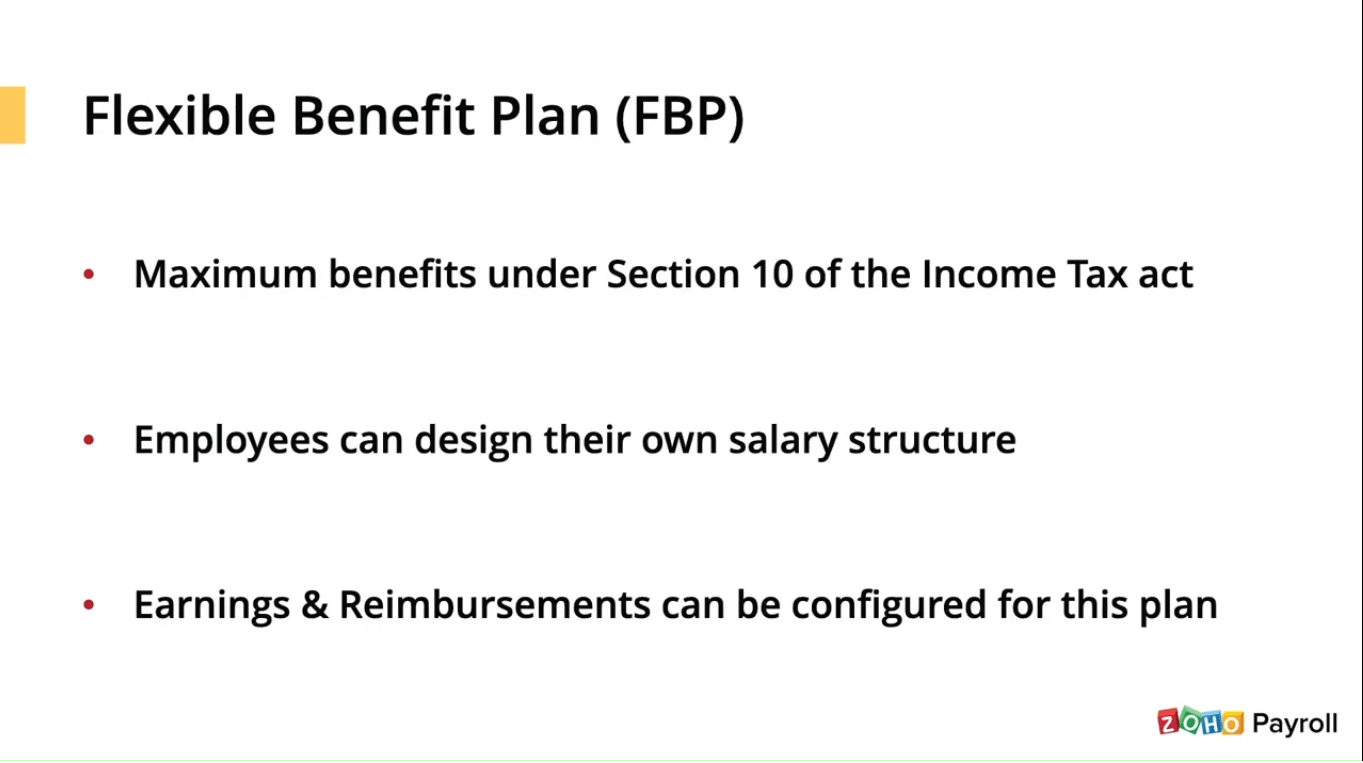
CTC reimbursements are for the personal expenses done by the employee in a month for employees belonging to higher tax labs. CTC reimbursements help in reducing the taxable income to an extent. The employee has to raise a claim by submitting the appropriate bills as proof of their expense and should be sent for the organization’s approval. Once the organization approves, the reimbursement gets paid out to the employees without any tax being attracted to it. About three other main categories under the salary components outside of this, there’s a concept called flexible benefits plan. A flexible benefits plan is designed to provide employees with a maximum income tax benefit. You can allow employees to design a portion of the salary structure by selecting the earnings and reimbursements from the list of the ones offered by you under this plan.
The Basics of Statutory Benefits
They are government-based schemes that look after the welfare and well-being of employees during employment. These statutory schemes also benefit the employee post their retirement from service.
There are three main statutory benefits employee provident fund, employees state insurance, and labor welfare fund.
Employee provident fund: this scheme provides social security to the employees post their retirement. Both employees and employers need to make an equal contribution of twelve percent towards this fund every month.
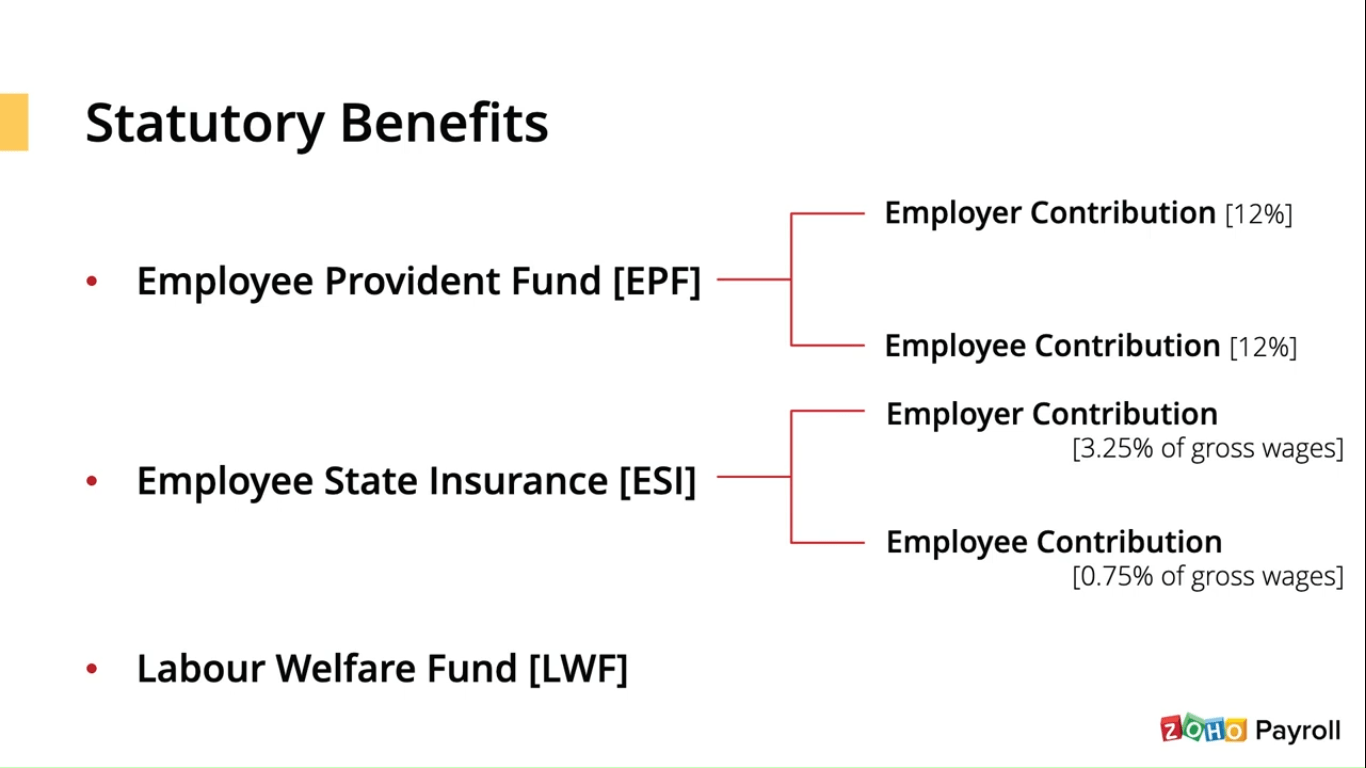
Employee state insurance: this scheme provides employees and their dependents with health insurance policies at lower premium rates employees earning a monthly income of rupees, twenty-one thousand or less, are eligible for this scheme—revised overall ESA contribution. Rate is 4% of the foreperson, 3.25% is the insurance premium worn by the organization, and the employee bears the remaining 0.75%.
Labor welfare fund: labor welfare fund was introduced in 1965 to improve the laborers working conditions and provide social security that can help improve the standard of living for the employees. The benefits cover education, medical facilities, food, transportation, and recreation. A labor welfare fund is a state-specific strategy managed by individual state authorities. Some states do not support the labor bill for the fund.
These three components and statutory components that we have seen until now are the monetary benefits provided to an employee as a part of the salary. But as an organization, you can provide your managers or directors with non-monetary benefits like company accommodation, company vehicle, company-provided helper, etc. Although these are not part of the salary structure, the employee must pay income tax for the asset’s value. This concept is known by the term poker sites.
How Can These Components Be Created in The Zoho Payroll?
To create your very first salary component, navigate to settings. Click on salary components. Under the earnings tab, you will see a predefined set of commonly used allowances, which you can use. If you want to create a new allowance type, click the add component option. From the drop-down, click earning. Select the earning component from the predefined list in the new earning screen since different organizations follow different naming conventions. For the allowances, you can personalize the learning component name and give it another name for the same component when it reflects in the pay slip. Click mark as active and click save.
This newly, created, earning component will now reflect in the earnings tab by default. Choose custom allowances if you do not find the elements you want to offer from the predefined earning list. Custom allowances give you more flexibility to create components based on payment type, fixed or variable and calculation type, flat amount, or the possibility of basic.
On the right-hand side, you will have other options like calculating allowances on a pro data basis, etc. Click mark as active and click save.
Deductions
There are pre-tax and post-tax deductions; navigate to settings to create a pre-tax deduction. Click salary components. If you want to create a pre-tax deduction, from the deductions tab, click add component option. From the drop-down, click pre-tax deduction. On this page, the deduction plan is prefilled. In the next drop-down, you can choose the investment plan so that employee gets an income tax benefit on this deduction under the selected section of the income tax act. This field is not mandatory and can be left blank if no exemption needs to be given to the employee.
You can also allow the application to calculate this deduction based on the employee’s working days in a month. So once all these configurations are made, click on mark as active and save.
Reimbursements
Reimbursements, as discussed earlier, provide employees with income tax benefits. Different categories of reimbursements you see on the screen are approved by the income tax department and reconfigured in the Zoho payroll. The setup that needs to be done with the reimbursement is to configure if it’s a part of the flexible benefits plan, along with the maximum limit per month allowed for the employees to claim. You can mark this as active and click on save to activate this component.
Statutory Benefits
As an organization, you might be worried about meeting all the strategy complaints with correct calculations at the time of payment every month. To keep you out of this, we have built Zoho payroll to automate calculations for statutory compliance. All you would require is a one-time setup of the sub-policies you follow in your organization for access—the setting of statutory benefits. You can navigate to settings. Click on statutory components. Here. First, let’s look at the setup of employees’ provident fund. When you click on enable button, the first two drop-downs are for setting up the employee and employer contributions. You can choose the configuration from the drop-down as 12% of the pf wages. Or you can also restrict the contribution to 15,000 of the pf wages.

Join Our Newsletter for the Latest Zoho News
Most recent news articles on Zoho from across the world. Includes press coverage of the most recent global Zoho launches and announcements.



